Russian Government Fires Geneticist Who Claimed Humans Used to Live for 900 Years

Russia’s Ministry of Education and Science recently fired the director of the prestigious Institute of General Genetics of the Russian Academy of Sciences allegedly for controversial remarks that are incompatible with science. Geneticist Alexander Kudryavtsev was named director of the General Genetics of the Russian Academy of Sciences in June of 2021 and was scheduled […]
Ready to Cook – The Controversial World of Featherless Chicken
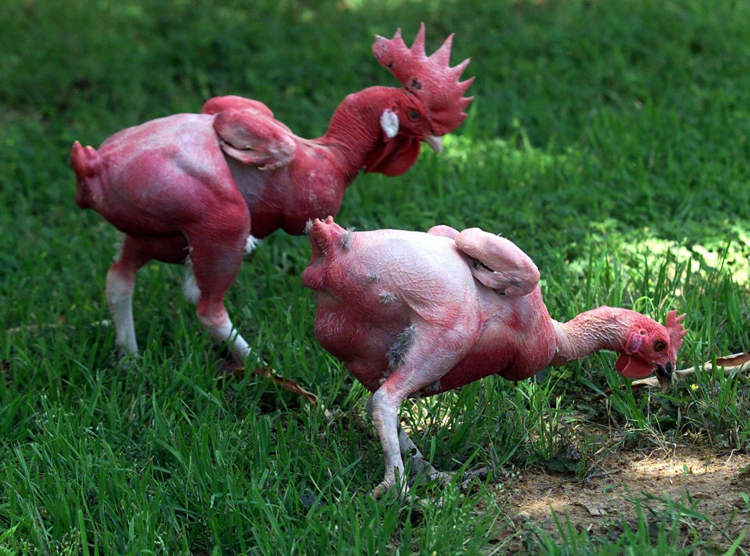

Featherless chicken is a relatively new breed of poultry created through selective breeding in order to combat a very common problem – overheating. However, the so-called ‘naked chickens’ have yet to become mainstream. Commercial broiler chickens are genetically prone to eat more and gain weight very fast which causes their body metabolism to operate at […]
Genetically-Modified Plants Glow When They Are Stressed
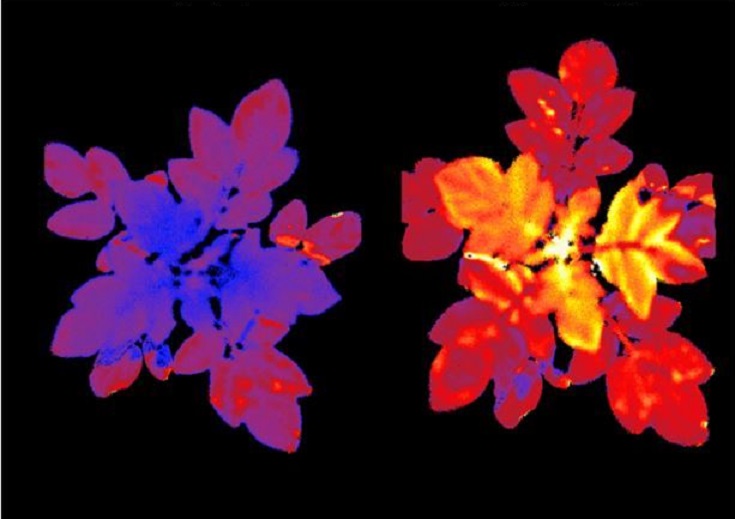
A team of researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem has managed to genetically modify potato plants to glow under fluorescent cameras when stressed by various factors. One of the biggest challenges of modern agriculture is reacting to stress factors before it’s too late. Plants don’t really have a way of conveying how they feel, […]
Researchers Find Extremely Rare Half-Male, Half-Female Bird Specimen
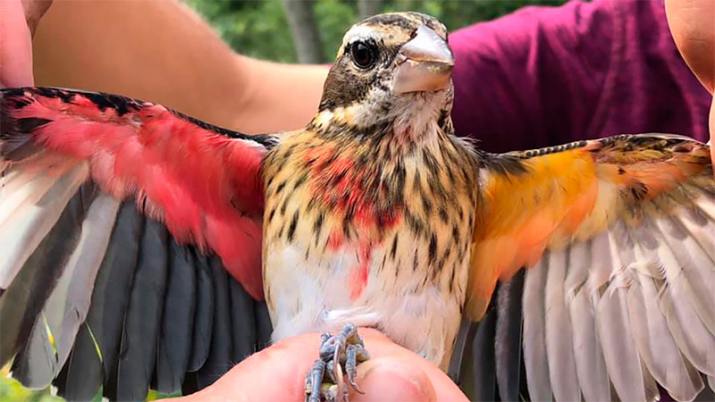

Researchers at the Powdermill Nature Reserve in Pennsylvania recently came across a “once in a lifetime discovery” – a half-male, half-female rose-breasted grosbeak. Annie Lindsay and her colleagues at Powdermill Nature Reserve were catching and banding birds with identification tags on September 24, when a fellow researcher called her over via walkie-talkie to supposedly see […]
Rare Genetic Mutation Makes Woman Virtually Immune to Pain, Anxiety and Stress

Jo Cameron, 71-year-old woman from Scotland, is one of only two people in the world known to have a rare genetic mutation that makes them virtually immune to pain. Interestingly, Cameron only learned about her “superpower” at age 65, when doctors found that she didn’t need any painkillers after a undergoing a serious operation on […]
Chinese Scientist Claims to Have Created the World’s First Genetically Edited Babies

Chinese researcher He Jiankui recently shocked the entire world after revealing that he had altered the DNA of twin girl before birth, to make them immune to the HIV virus and AIDS. If his claims prove to be true, these twins would be the world’s first genetically-edited babies. Professor He revealed his controversial genetic editing […]
Belgian Blue Cattle – Bodybuilders of the Bovine World

Belgian Blue cattle may look like they’ve spent most of their lives pumping iron, but they owe their double muscle characteristics to years of careful breeding and genetics. Like the name implies, this incredible bred of cattle originated in Belgium. In the second half of the 19th century, Shorthorn bulls from the United Kingdom were […]
Japanese Researchers Create Tweeting Mouse

In a genetically engineered experiment, Japanese scientists at the University of Osaka have created a mouse that tweets like a bird. After crossbreeding genetically altered mice for some time, to see what would happen, they apparently got their first interesting result, by mistake. Researcher Arikuni Uchimura said they were expecting physical mutations, but definitely not […]
