The Curious Case of a Man Who Cannot See Simple Digits From 2 to 9
Scientists at Johns Hopkins University recently reported the strange case of a man’s whose rare degenerative brain disease left him unable to distinguish basic numbers from 2 to 9. After studying an engineering geologist diagnosed with a rare degenerative brain disease called corticobasal syndrome for eight years, researchers published a study which they claim suggests […]
Concerning Number of Americans Drinking and Gurgling Bleach to Prevent Covid-19
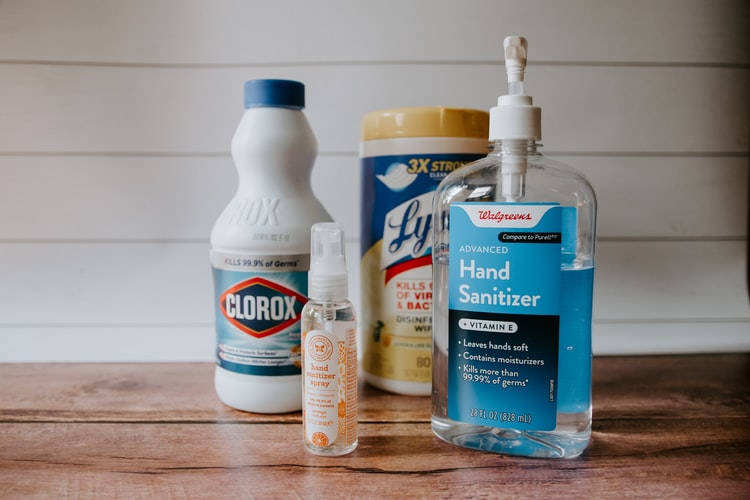

The results of a recently-published survey conducted by the Center for Disease Control (CDC) suggest that 39 percent of Americans are using bleach and other high-risk cleaners in improper ways in order to prevent getting infected with the novel coronavirus. After noticing an unusual spike in calls to poison control center about harmful exposures to […]
London Lab Offers People $4,500 to Get Voluntarily Infected with Coronavirus
As part of a global effort to find a vaccine for the Covid-19 coronavirus, pharmaceutical companies are offering thousands of dollars to people willing to voluntarily get infected with a form of the virus and spend two weeks in isolation. Being the first to come up with an effective vaccine for Covid-19 would undoubtedly prove […]
French Researchers Build Creepy Phone Case That Mimics Human Skin
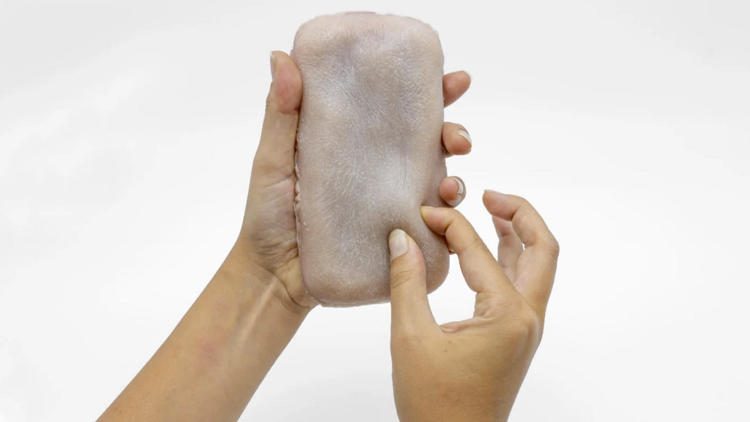

A team of French and English researchers recently showcased a prototype phone case called Skin-On, which not only mimics the look and feel of human skin, but also enables interaction communication through gestures like pinching or tickling. Developed by researchers at the University of Bristol in partnership with Telecomm ParisTech and Sorbonne University, Skin-On consists […]
Cockroach Milk Could One Day Become the Ultimate Superfood

Consuming a fluid secreted by cockroaches may not be everyone’s idea of a balanced meal, but scientists believe that the “cockroach milk” produced by a certain species of cockroaches is one of the most nutritious substances on the planet, and could one day become the ultimate superfood. Unlike most other insects, the Pacific beetle cockroach is viviparous, […]
Scientists Develop Eye-Drops That Could Repair Eye Damage, Make Glasses Unnecessary

Scientists at Bar-Ilan University’s Institute of Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials, in Tel Aviv, Israel, claim to have created some truly revolutionary eye-drops that can heal damaged corneas and improve vision. Described as “a new concept for correcting refractory problems”, the nanodrops developed by ophthalmologist Dr. David Smadja and a team of scientists from Shaare Zedek Medical Center and Bar-Ilan […]
Australia’s “Firehawks” Deliberately Start Wildfires to Flush Out Prey
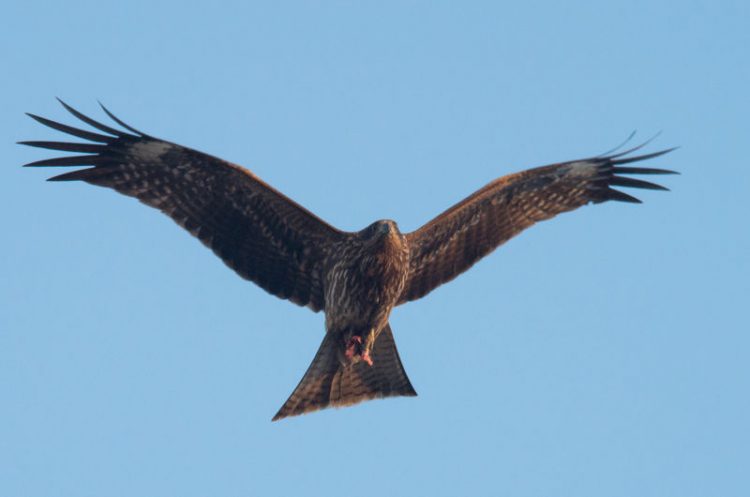

According to a research paper published recently in the Journal of Ethnobiology, several Australian birds of prey have the habit of starting wildfires for the soul purpose of flushing out prey from the blazing grasslands. Interestingly, aboriginals have known about this for over 40,000 years and even have a name for the fire-wielding birds – […]
MIT Scientists Develop Method to Make Plants Glow in the Dark
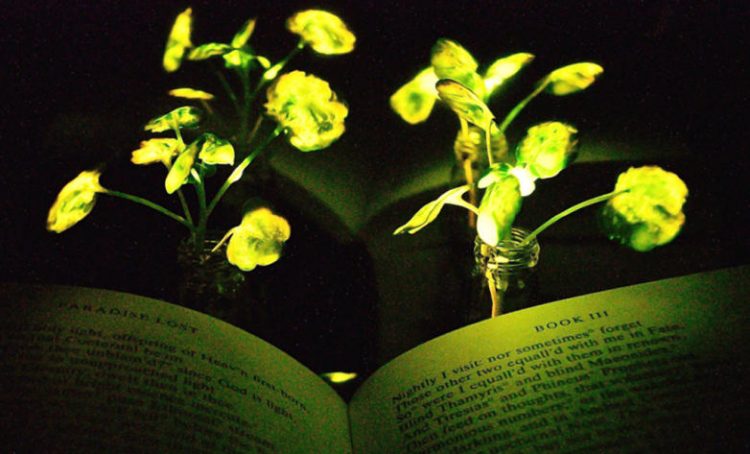

MIT researchers have made an important breakthrough in their quest to make plants that glow in the dark a reality. In what they call Plant Nanobionics, the engineers embedded nanoparticles into the leaves of a watercress plant that caused the plants to give off a dim glow for three and a half hours. Their next […]
New Cancer Drugs Turn Patients’ Gray Hair Dark Again
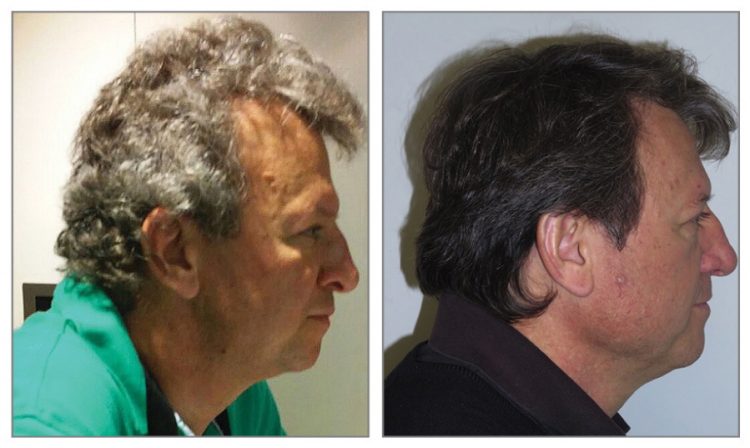
Cancer therapy is known to cause patients’ hair to fall off, but a few new cancer drugs apparently have a completely different side effect – they restore pigment in older people’s gray hair. Spanish researchers testing three new cancer drugs – Keytruda, Opdivo and Tecentriq – for negative side-effects in cancer patients made a very surprising discovery. After […]
Man Has Spent the Last 40 Years Living Alone in Colorado Ghost Town Recording All Kinds of Useful Data

For the past four decades, billy barr – he insists his name be written with lower case letters only – has been living by himself in Gothic, Colorado, a ghost town deserted since the 1920s, passing the time by recording all sorts of data, from daily snowfalls, temperatures, snow melting, animal sightings, etc.. He never imagined […]
Scientists Draw Eyes on the Butts of Cows to Protect Them from Lions
It might sound like a silly idea, but it turns out that drawing eyes on the rumps of cattle might deter lions from attacking and prevent human retaliation against the mighty predators. It sounds like a strategy to protect the poor cattle, but the idea is actually to protect endangered African lions from human retaliation. The […]
Scientist Creates Possible Cure to All Viruses, Needs It to Go Viral
When MIT-trained engineer Todd Rider revealed his revolutionary idea for killing virtually any virus, everyone from fellow scientists to The White House praised him for his results, with some going as far as to call his discovery the most important medical breakthrough since antibiotics. Yet four years later, Rider is struggling to find funds for his research […]
Researchers Create Transparent Wood That Could One Day Replace Glass in Windows
It may seem inconceivable, but believe it or not, there really is such a thing as transparent wood. After decades of work, scientists at the KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm have finally managed to create a viable material that, if mass produced, holds the potential to revolutionize architecture and solar technology. According to researchers, transparent […]
Swedish Scientists Want to Find Out if Cats Meow with an Accent Based on Where They Live
A cat with an accent sounds like a character in a whimsical children’s tale, but Swedish scientists are trying to figure out if domestic cats actually do have differing ‘dialects’ based on their geographical location. They also want to understand if the owner’s voice might have a role to play in the way cats’ meow. If […]
Scientist Volunteers as All-You-Can-Eat Buffet for Bedbugs in the Name of Science
In a bid to find a remedy for bedbugs, Canadian scientist Regine Gries has spent nearly a decade studying the parasitic creatures. In fact, she is so dedicated to the project that she actually allows thousands of hungry bedbugs feast off her own blood! Thankfully, her efforts have paid off – she and her husband […]
