Scientists Unravel Centuries-old Mystery of Cannon-Like Boom Emanating from Lake
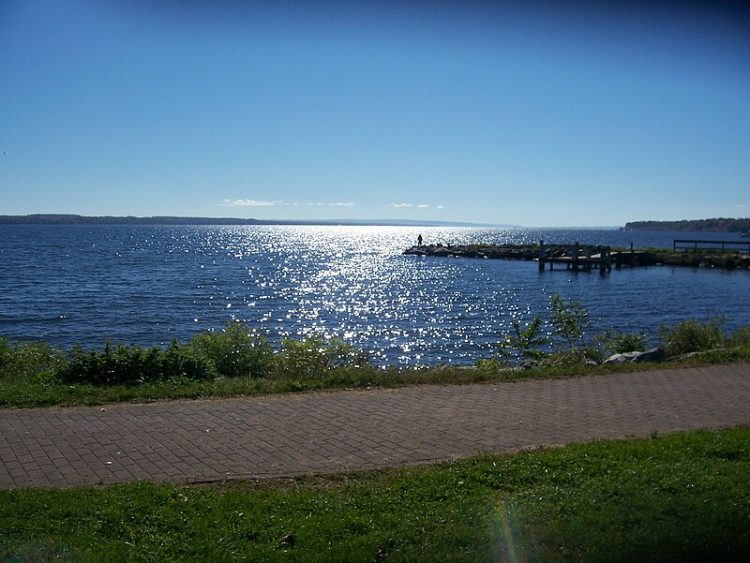

For centuries, scientists have been puzzled by the mysterious phenomenon known as “Seneca’s Gun”, a loud boom emanating from New York’s Seneca Lake. Records of loud explosions heard on Seneca Lake date back to the 17th century, but they had become the subject of myth and folklore long before that. The Seneca people, a Native […]
Listening to the World’s ‘Sweetest Melody’ Makes Chocolate Taste Better
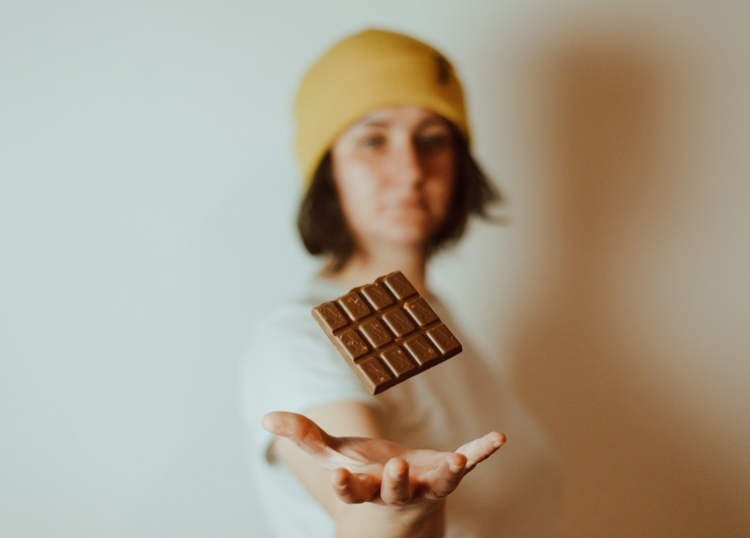

A sound expert at the University of Bristol in the UK created a special song designed to enhance the sweetness and intensity of chocolate. The “Sweetest Melody” is the result of over 60 years of scientific research into a phenomenon known as “multisensory integration,” where taste and hearing influence each other. Apparently, music with soft […]
Scientists Create World’s First Cyborg Bee with Ultra-Light Brain Controller
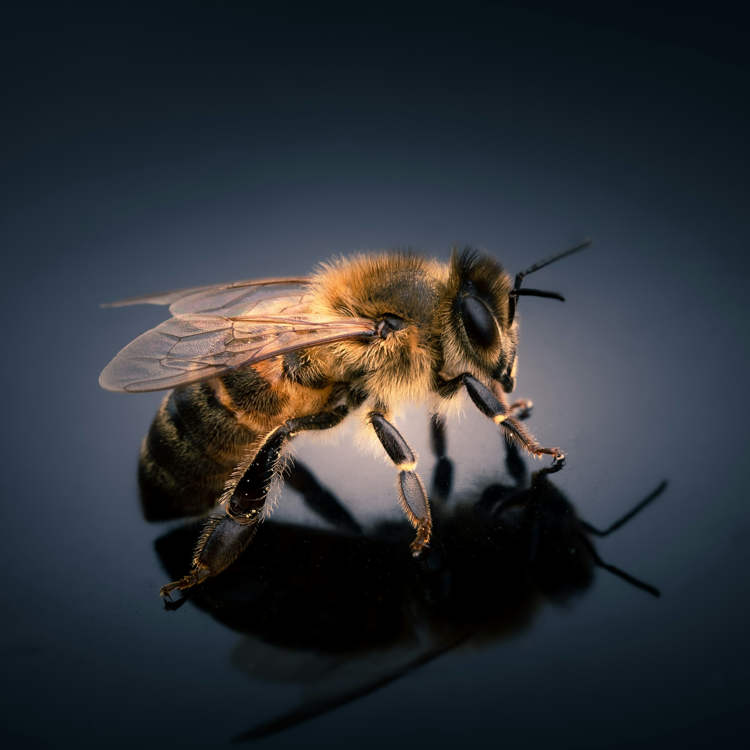

Scientists at the Beijing Institute of Technology used a 74-milligram insect brain controller to create the world’s first cyborg bee. Worker bees can carry nectar sacks weighing about 80 per cent of their body mass for 5 km (3 miles) without resting, so they have no problem carrying a 74-milligram brain controller developed by Chinese […]
Scientists Discover Tree That Thrives When Struck by Lightning
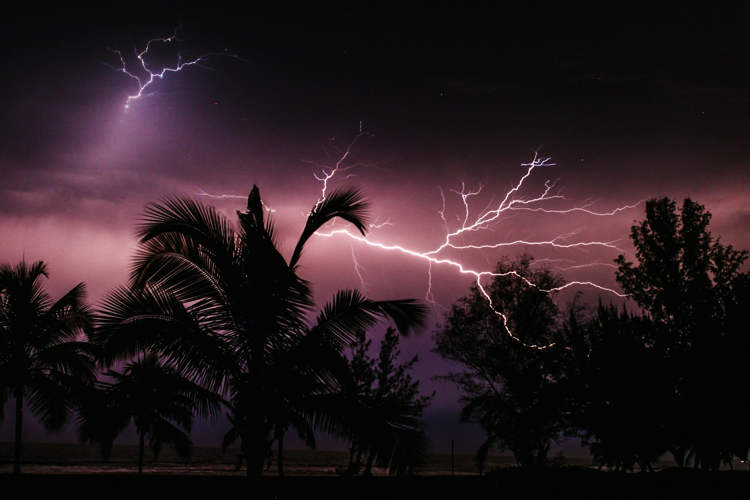

Lightning kills most of the trees it strikes, but scientists have discovered a tree species that not only survives lightning strikes but thrives as a direct result of them. For the longest time, there was a consensus in the scientific community that lightning could only have negative effects on trees. In the best case scenario, […]
Fish the Size of a Human Fingernail Is as Loud as a Jet Engine
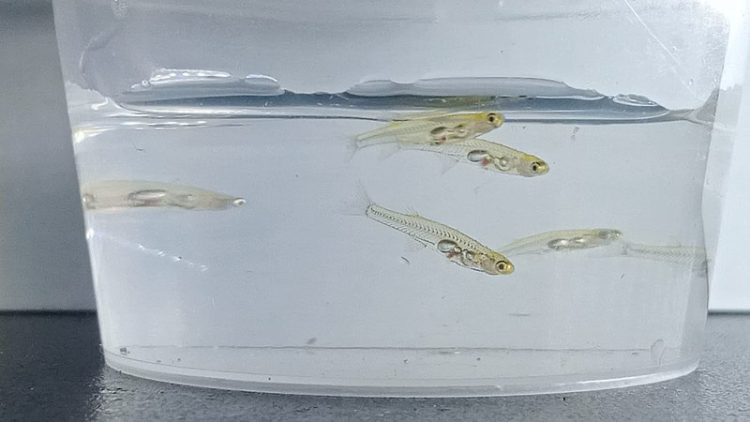

Danionella cerebrum, a translucent fish only 12mm in size can produce sounds exceeding 140 dB, comparable to the sound perceived by a person standing 100 m from a passenger jet during take-off. Danionella cerebrum fish were originally identified in the 1980s, but the species was officially recognized in 2021 after scientists discovered subtle physical differences […]
World’s Lightest Handbag Is 99 Percent Air, Weighs Only 37 Grams

French fashion brand Coperni recently unveiled a unique version of its iconic Swipe bag made from the lightest solid material on Earth, aerogel. Named ‘Air Swipe’, the accessory weighs only 37 grams. Every year, Coperni recreates its popular Swipe bag in a unique, thought-provoking way. Last year, they created a limited-edition “meteorite’ handbag hand-carved from […]
South-Korean Researchers Create Beef-Infused Super Rice

Scientists at South Korea’s Yonsei University have created a new type of hybrid rice that not only has a meaty pink color but is also packed with beef protein and fat cells. Rice is already one of the most nutritious foods available in nature, but thanks to some scientific ‘magic’, it could soon become a […]
Scientists Baffled by Mushroom Growing on Live Frog
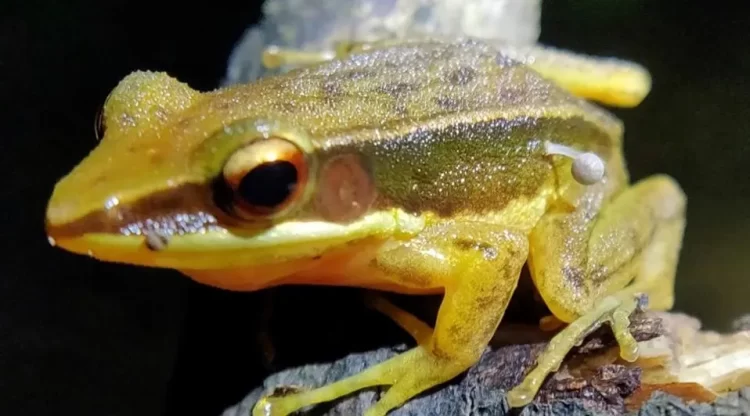

In what is believed to be the first ever such documented case, researchers in India came across a live frog with a small mushroom growing on the side of its body. The Last of Us, the hit HBO series based on the namesake video game series, has popularized the fictional idea of mushrooms and fungi […]
Russian Government Fires Geneticist Who Claimed Humans Used to Live for 900 Years

Russia’s Ministry of Education and Science recently fired the director of the prestigious Institute of General Genetics of the Russian Academy of Sciences allegedly for controversial remarks that are incompatible with science. Geneticist Alexander Kudryavtsev was named director of the General Genetics of the Russian Academy of Sciences in June of 2021 and was scheduled […]
China Builds World’s Deepest Underground Laboratory to Study Dark Matter
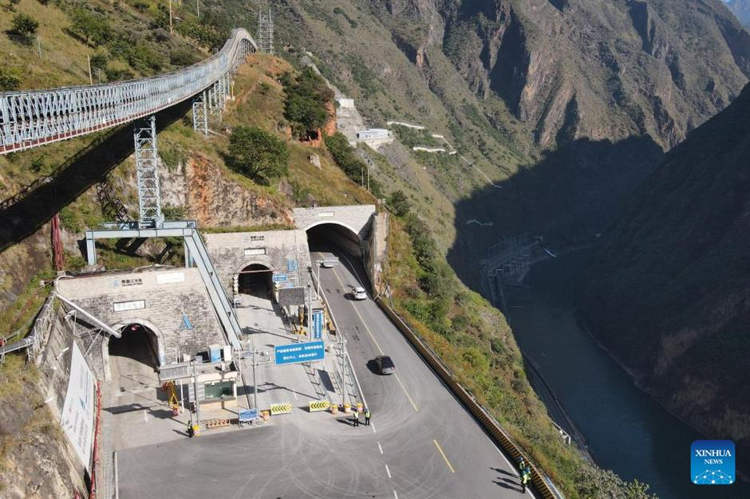

Located 2,400 meters under the Earth’s surface, the Deep Underground and Ultra-low Radiation Background Facility for Frontier Physics Experiments (DURF) is the world’s deepest underground laboratory. In December 2020, Tsinghua University and Yalong River Hydropower Development Company, Ltd. began work on a daring project under Jinping Mountain in Sichuan’s Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture. Designed to […]
Chinese Scientists Develop Ultra-Slippery Toilet Bowl That Almost Nothing Sticks To
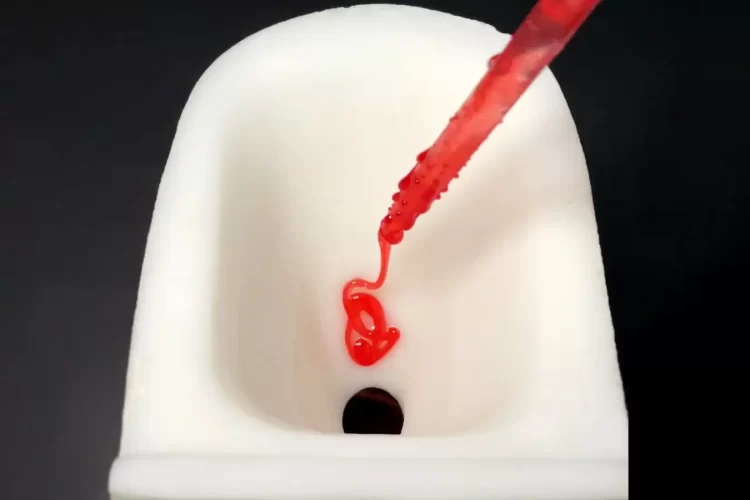
Chinese scientists at the Huazhong University of Science and Technology in Wuhan have developed a new, ultra-slippery toilet bowl that almost nothing sticks to. Porcelain has been the most common toilet bowl manufacturing material for quite a while now, and while it may be a while before a new material upsets it, we already have […]
Researchers Find That Birds Are Using Anti-Bird Spikes to Build and Protect Their Own Nests
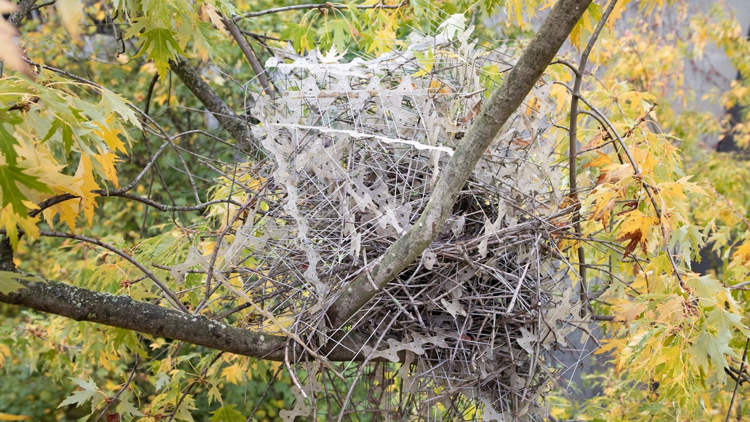

A team of Dutch researchers has discovered that magpies and crows are using metal spikes designed to keep them away from certain urban areas to reinforce their own nests and keep intruders at bay. Scientists have known for a while that magpies and crows are some of the most intelligent birds in the world, but […]
Newly Discovered Species of Palm Tree Flowers and Bears Fruit Underground
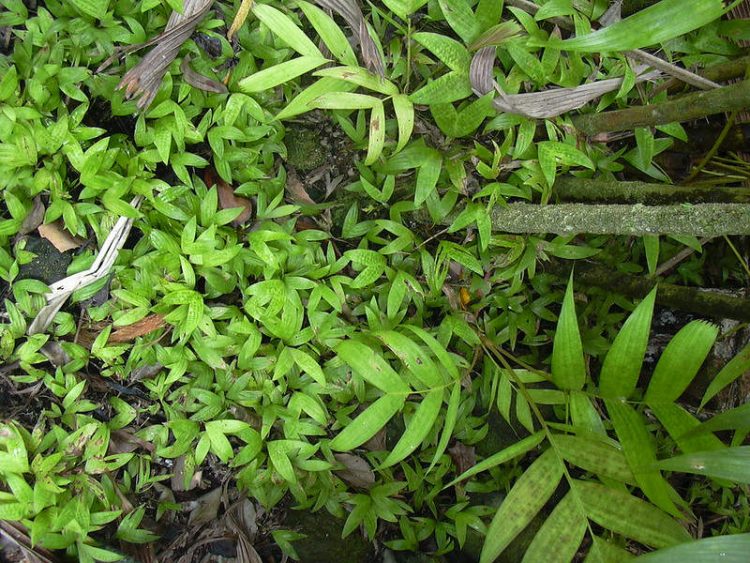

Pinanga subterranea, a new species of palm discovered by researchers at the Royal Botanic Gardens, is one of only two known plants that exclusively fruit and flower underground. There are more than 2,500 species of palm known to science, but Pinanga subterranea, a new species discovered on the tropical island of Borneo, is the only one that […]
Scientists Create ‘Superbanana’ That Could Save Millions of Lives

An international team of scientists has reportedly created a genetically-modified ‘superbanana’ that contains significantly more nutrients, especially vitamin A. Vitamin A deficiency has been plaguing poor countries in sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia for hundreds of years, inhibiting children’s growth, causing blindness and significantly weakening their resistance to deadly treatable diseases such as diarrhea and […]
Man Is Living Underwater for 100 Days to See How It Affects His Body and Mind

A Florida University professor plans to spend 100 days 30 feet under the ocean’s surface, in an underwater lodge, as a scientific experiment to find out how the constant increased pressure affects his body and mind. The current world record for time spent living underwater was set in 2014 by two Tennessee biologists who managed […]
