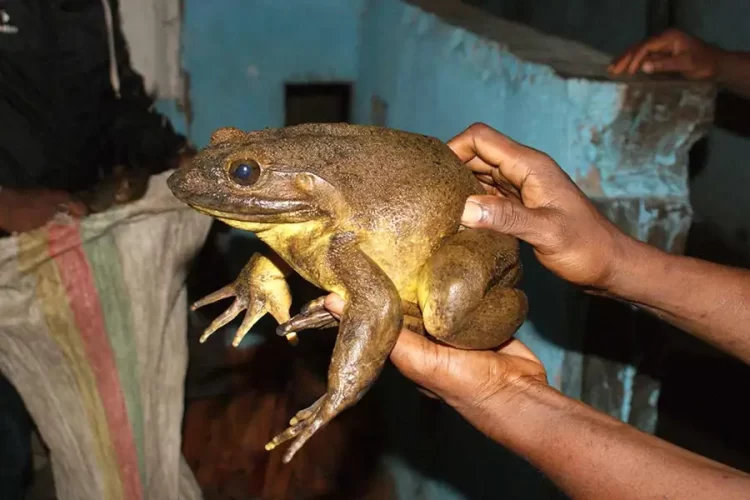
The Goliath Frog, the largest living frog on Earth, is facing extinction after a 50% decline in population size in the last three generations, mainly due to human activity.
The Goliath Frog certainly lives up to its name. Reaching up to 13 inches long (32 cm) from snout to vent, and weighing up to 7.2 lb (3.25 kg), it is by far the world’s largest frog. However, it has a contrastingly tiny habitat range in Africa’s Cameroon and Equatorial Guinea, which makes it particularly vulnerable to human-related habitat destruction. They are skittish creatures that tend to avoid humans as much as possible, but increasingly sophisticated traps and habitat destruction have caused a massive decrease in the number of Goliath frogs, and experts warn that if things don’t change soon, this impressive creature will become extinct.